In today’s digital world, businesses thrive on information and connectivity. Because of this, cybersecurity and risk management have become the lifeblood of any organization. A single cyber-attack can sink a company faster than a rogue wave. They’re about creating a comprehensive strategy to identify, assess, and mitigate the risks that threaten your business. But what exactly are they, and how can you ensure your business is well-prepared to face the challenges of the digital age? Stick around, and let’s unravel this together.
Understanding Cybersecurity Threats
It’s not a matter of if but when a company will encounter a digital threat. A frozen computer screen demanding a ransom, an email from your “bank” requesting sensitive information, or a sudden website outage are all too standard in today’s digital landscape.
Here are the most prevalent cyber threats that can cripple a business:
Malware
This malicious software is a chameleon, disguising itself as viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware. It infiltrates systems through seemingly innocuous email attachments, compromised websites, or USB drives.
Data Breaches
These are the digital equivalent of a break-in, where hackers penetrate your defenses to access confidential data. Customer information, financial records, and intellectual property are all valuable targets for cybercriminals.
Insider Threats
Disgruntled employees, careless staff, or even external contractors can, either intentionally or unintentionally, compromise your cybersecurity.
The sheer variety and complexity of cyber threats can be overwhelming for businesses. Fortunately, a dedicated IT support team can be your secret weapon. They possess the expertise to assess your vulnerabilities, implement robust security measures, and swiftly respond to incidents, minimizing the damage and ensuring business continuity.
Aside from those mentioned, here’s another prevalent threat:
Phishing Attacks
These cunning social engineering schemes manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information, such as passwords, credit card details, or social security numbers. They often masquerade as legitimate emails, texts, or phone calls from trusted sources. Some of the biggest DNS attacks have also employed similar deceptive tactics to redirect users to malicious websites, further underscoring the importance of proactive security measures.
For businesses that lack the resources or expertise to manage cybersecurity in-house, managed cybersecurity services can provide a lifeline. These services provide comprehensive protection, encompassing threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management, enabling you to concentrate on your core business operations.
Core Components of a Cybersecurity Strategy
A robust cybersecurity strategy involves people, processes, and a proactive mindset. Here are the steps to take in a cyber-attack:
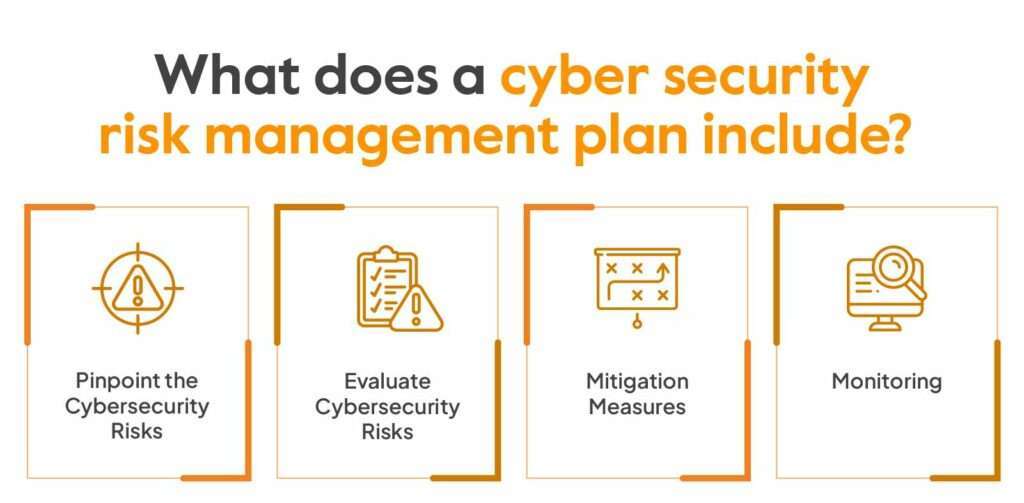
Risk Assessment
A risk assessment involves identifying your most valuable assets (customer data, financial information, intellectual property) and the potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
Prevention
Prevention involves implementing measures to prevent cyberattacks before they occur. This includes:
- Strong Passwords: Encourage employees to use and change solid and unique passwords regularly. You can even implement a password manager to make things easier.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This method adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second verification form, such as a code sent to their phone and their password. It is an effective way to verify your customers’ identity and ensure that only authorized individuals gain access.
- Firewall: These control incoming and outgoing traffic on your network.
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: These tools scan your systems for malicious software and block it from causing harm.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your software updated to patch any security holes that hackers could exploit. To strengthen this practice across complex, multi-cloud environments, automated tools continuously scan for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Cloud Security Posture Management provides visibility and enforces compliance across cloud platforms, helping reduce risks and improve security posture continuously.
- Employee Training: Educate your staff about cybersecurity risks and best practices. This includes how to spot phishing emails, create strong passwords, and report suspicious activity.
Detection
Detection is monitoring your systems for any signs of unauthorized activity. This can be done through:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: These tools collect and analyze data from your network and systems to detect suspicious activity.
- Network Monitoring: Monitor your network traffic for unusual patterns indicating an attack.
- Vulnerability Scans: Regularly scan your systems for vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit. Many organizations also use a purple team in cybersecurity to test their detection capabilities, where offensive and defensive teams work together to identify gaps in monitoring systems.
Response and Recovery
No matter how careful you are, there’s always a chance that an attack could succeed. That’s why it’s crucial to have a plan in place for how to respond and recover. This includes:
- Incident Response Plan: This outlines the steps to take in a cyber-attack, including who to contact, how to contain the damage, and how to restore your systems.
- Data Backups: Regularly back up your critical data to a secure location so you can restore it if it’s lost or compromised.
- Cyber Insurance: This can help cover the costs of a cyber attack, such as legal fees, data recovery, and customer notification.
Building a solid cybersecurity strategy takes time and effort but is an investment in your business’s future.
Risk Management Beyond Technology
While technology plays a crucial role in risk management, it’s equally important to address the risks that arise from human factors and know how to manage risks and fraud. These can include:
Employee Error
Mistakes happen, but human error can lead to data breaches, financial loss, or operational disruptions. Implementing thorough training programs, clear procedures, and checks and balances can mitigate these risks.
Internal Fraud
Unfortunately, employees may sometimes engage in fraudulent activities. Strong internal controls, regular audits, and fostering a culture of ethics can help deter and detect such behavior.
Third-Party Risk
Businesses often rely on vendors, suppliers, or partners who may introduce their risks. Due diligence in selecting and monitoring third parties is essential.
Compliance Risks
The ever-evolving landscape of regulatory requirements presents a persistent challenge for businesses. Non-compliance will result in significant legal repercussions and tarnish a company’s reputation.
Reputation Risk
Negative publicity – news of a data breach that makes you shake your head in disbelief, a flurry of customer complaints, or a social media firestorm – can tarnish a company’s reputation overnight. Proactive reputation management is no longer optional. It’s essential to monitor online conversations, address concerns promptly, and engage in transparent communication to mitigate the impact of adverse events and safeguard your brand’s image.
By acknowledging and addressing the human element in cybersecurity and risk management, organizations can create a more robust defense against potential threats.
Strategies for Managing Non-Technological Risks
Here are some effective strategies to mitigate non-technological risks:
Culture of Risk Awareness
Encourage employees at all levels to be vigilant about potential risks and promptly report any concerns.
Robust Policies and Procedures
Establish clear guidelines for how employees should handle sensitive data, interact with third parties, and report suspicious activity.
Regular Training
Provide ongoing training to employees on security best practices, compliance requirements, and ethical behavior.
Background Checks
Conduct thorough background checks on potential employees, especially those in sensitive positions.
Organizations can create a more comprehensive risk management strategy that protects their assets, reputation, and long-term success by addressing technological and non-technological risks.
Additional Considerations for Small Businesses
Small businesses often face unique cybersecurity and risk management challenges due to limited resources and expertise. However, proactively addressing these considerations can help them mitigate potential threats:
Resource Constraints
Prioritizing essential safeguards, such as strong passwords, data backups, and basic cybersecurity measures, can provide a good foundation.
Cybersecurity Awareness
Implementing regular cybersecurity training and staying informed about emerging risks can help protect against attacks.
Data Protection
Data protection measures, such as encryption, access controls, and secure data disposal, can prevent breaches and maintain customer trust.
Insurance Coverage
Small businesses can benefit from insurance policies tailored to their specific risks, such as general, professional, and cyber liability insurance.
External Expertise
Consider partnering with external consultants or service providers specializing in risk management to supplement internal capabilities.
By recognizing these unique challenges and taking proactive steps, small businesses can create a resilient risk management strategy that safeguards their operations and ensures long-term success.
Final Thoughts
In today’s interconnected world, risk is an ever-present reality. Yet, with a well-rounded cybersecurity and risk management proactive approach, organizations of all sizes can transform these challenges into opportunities for growth and resilience. The future belongs to those who understand and embrace the complexities of risk, safeguarding their assets, reputation, and, ultimately, their path to success.
Are you ready to take the next step in fortifying your organization?








